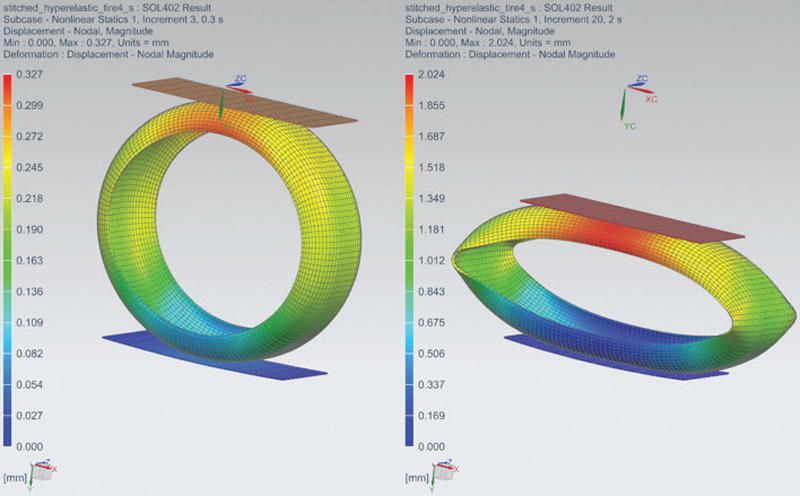
Both NX Nastran Multistep Nonlinear solutions also have very robust solution algorithms and efficiently obtain converged solutions for some of the most difficult and intractable nonlinear models. The input and output formats for SOL 401 and 402 are also very similar and it is very easy to set up a Nastran model to run for either solution. These solutions offer the following capabilities.
Major capabilities
Solution step types
- Static
- Dynamic
- Preload
- Modal
- Buckling
- Cyclic symmetry modes
- Fourier harmonic modes
Contact
- Shell and solid element face contact
- Edge contact for axisymmetric modeling
- Single- and double-sided contact
- Self-contact
- Multiple friction models
- Tied contact
- Contact surface offsets
- Gap elements
Contact activation/deactivation per subcase
• Contact pressures and force results
• Contact separation and sliding results
Geometric nonlinear
- Large deformations
- Large strain
- Snap-through analysis (post-buckling)
- Follower forces
Material nonlinear
- Hyperelasticity modelsMooney-Rivlin
- Ogden
- Hyperfoam
- Mullins effect
- Damping with Prony series
- Elasto-plasticVon Mises yield criterion
- Isotropic hardening
- Kinematic hardening
- Mixed hardening
- Thermal elasto-plastic
- Creep
- Plasticity
- Strain measures: engineering, logarithmic
- Combined creep and elasto-plastic
Composite modeling
- Ply layers for solid or shell elements
- Failure indices
- Strength ratios
- Cohesive delamination
- Progressive damage
Element types
- 2D and 3D solids
- Shell
- Beams
- Springs and bushings
- Rigid
- Mean elements (RBE3)
- Plane stress
- Plane strain and generalized plane strain
- Chocking
Other modeling capabilities
- Fixed and sliding glue connections
- Cyclic symmetry boundary conditions
- Mesh imperfections
- J-integral for crack simulation
- Co-simulation with thermal solver
Robust solution methods
- Full Newton iterations, with or without line searches
- Arc length solution method
- Automatic time stepping (ATS) method
- Energy, force and deformation convergence criteria
- Dynamic solution with Newmark method for direct implicit integration
- Sparse solver and iterative solver
- Stiffness stabilization for static solutions
- High-performance computing (HPC) on multiprocessors
Load conditions
- Bolt preload
- Concentrated loads
- Distributed loads
- Follower loads
- Pressure loads
- Inertia loads
- Enforced motion
- Applied temperatures
- Initial conditions for displacement, velocity and temperature
- Initial stress/strain conditions
- Edge load support for plain stress and plain strain elements